

Motorway 16, north of Copenhagen. Cycle tracks on either side. The discussion continues unabated, around the world, about whether the bicycle can perform as a transport mode at distances above 5 km and thus present itself as alternative for motorized vehicles. First, let’s consider this quote:
”In the late 19th century, large numbers of women were already using bicycles to get to work, women office workers and shop assistants wending their way each weekday morning from the suburbs to the town. They found the bicycle a convenient form of transport for distances up to, say, ten miles”.
Plucked from John Woodeforde's book ”The Story of the Bicycle”, 1970 So the bicycle as an effective performer at longer distances is nothing new. Nevertheless, we're relearning the bicycle story.
A published peer-reviewed conference paper (full version here - on google docs), based on my Masters’ degree thesis in Environmental Engineering (specializing in Urban Planning), included an assessment on the environmental, economic and time aspects regarding bicycle use on longer distances – in this case it was 15 km. To sum it up in a few words: yes, the bicycle is an option, even for longer distances. The one condition is having (at least) quality public transport of an average level.
The study was done in Lisbon, Portugal. For this part of the work, the following methodology was used: over a total of 33 days, data was collected regarding bicycle trips. Data such as time spent, costs, maximum speed, average speed, temperature, etc, was collected along the chosen routes. Despite the difficulties throughout the whole year of the thesis, I was fortunate to be the one creating, collecting and treating my own data -- this is a cyclist and data geek's nirvana. Nevertheless, here’s a small small preview of the data file: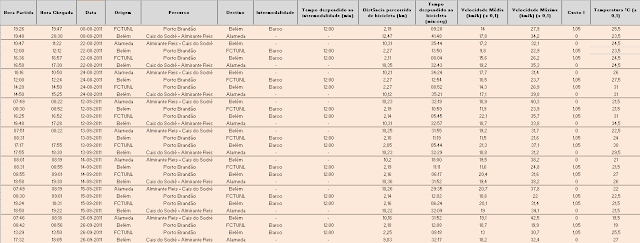 In this particular case, a river had to be crossed (from Lisbon to Almada) so the options to cross it were by train or ferry. The first and last sections of the the commute were by bicycle. After this fieldwork, a car trip was simulated in order to compare with the bicycle (and public transportation) use. Thus, the routes studied were the following:
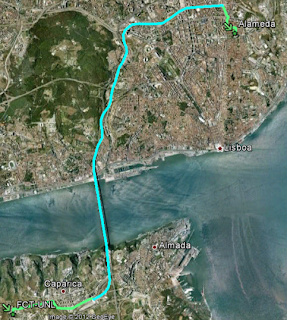
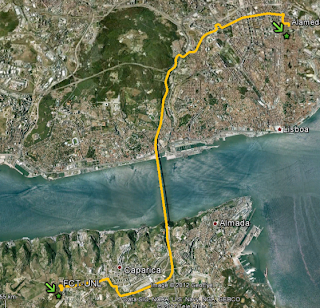
In this particular case, a river had to be crossed (from Lisbon to Almada) so the options to cross it were by train or ferry. The first and last sections of the the commute were by bicycle. After this fieldwork, a car trip was simulated in order to compare with the bicycle (and public transportation) use. Thus, the routes studied were the following:
 |
| Route: bicycle (green) + boat (red) |
 |
| Route: bicycle (green) + train (blue) |
 |
| Route: car commute simulation |
- Depending on the hour of commuting, the bicycle (used with the public transportation) was faster than the car;
- The bicycle combined with the train pollutes eight times less than the car. Combined with the ferry, pollutes six times less;
- Using the bicycle and the train would result in a cost saving four times greater than the car. With the ferry, the cost benefit was seven times greater than with the car;
- An average worker in Greater Lisbon works three days per month just to pay for his car.




